Dosing & Uses
Dosage Forms & Strengths
infusion solution
- 200mg/100mL
- 200mg/20mL
- 400mg/40mL
- 400mg/200mL
oral suspension
- 250mg/5mL
- 500mg/5mL
tablet
- 100mg
- 250mg
- 500mg
- 750mg
tablet, extended release
- 500mg
- 1000mg
Acute Sinusitis
Mild/moderate: 500 mg PO q12hr or 400 mg IV q12hr for 10 days
Limitations-of-use: Reserve fluoroquinolones for patients who do not have other available treatment options for acute sinusitis
Bone & Joint Infections
Mild/moderate: 500 mg PO q12hr or 400 mg IV q12hr for ≥4-6 weeks
Severe/complicated: 750 mg PO q12hr or 400 mg IV q8hr for ≥4-6 weeks
Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis
Indicated for chronic bacterial prostatitis caused by Escherichia coli or Proteus mirabilis
Mild/moderate: 500 mg PO q12hr or 400 mg IV q12hr for 28 days
Infectious Diarrhea
Mild/moderate/severe: 500 mg PO q12hr for 5-7 days
Empirical Therapy in Febrile Neutropenic Patients
Severe: 400 mg IV q8hr for 7-14 days
Intra-abdominal Infections
Complicated: 500 mg PO q12hr or 400 mg IV q12hr for 7-14 days
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections
Mild/moderate: 500 mg PO q12hr or 400 mg IV q12hr for 7-14 days
Severe/complicated: 750 mg PO q12hr or 400 mg IV q8hr for 7-14 days
Limitations-of-use: Reserve fluoroquinolones for patients who do not have other available treatment options for acute bacterial exacerbation of chronic bronchitis
Nosocomial Pneumonia
Mild/moderate/severe: 400 mg IV q8hr for 10-14 days
Skin/Skin Structure Infections
Mild/moderate: 500 mg PO q12hr or 400 mg IV q12hr for 7-14 days
Severe/complicated: 750 mg PO q12hr or 400 mg IV q8hr for 7-14 days
Urinary Tract Infections
Acute uncomplicated: Immediate-release, 250 mg PO q12hr for 3 days; extended-release, 500 mg PO q24hr for 3 days
Mild/moderate: 250 mg PO q12hr or 200 mg IV q12hr for 7-14 days
Severe/complicated: 500 mg PO q12hr or 400 mg IV q12hr for 7-14 days
Limitations-of-use: Reserve fluoroquinolones for patients who do not have other available treatment options for uncomplicated urinary tract infections
Urethral & Cervical Gonococcal Infections
Uncomplicated: 250-500 mg PO once
Anthrax Infection
Postexposure therapy
Inhalation (prophylaxis/postexposure): 500 mg PO q12hr or 400 mg IV q12hr for 60 days
Cutaneous: 500 mg PO q12hr or 400 mg IV q12hr for 60 days
Plague
Indication for treatment and prophylaxis of plague due to Yersinia pestis
500-750 mg PO q12hr x14 days, OR
400 mg IV q8-12hr x 14 days
Bronchiectasis (Orphan)
Orphan indication sponsor
- Aradigm Corporation, 3929 Point Eden Way, Hayward, CA 94545
Noncystic Fibrosis Bronchiectasis (Orphan)
Dry powder for inhalation: Orphan designation for patients with NCFB who suffer from frequent severe acute pulmonary bacterial exacerbations which lead to further inflammation, airway, and lung parenchyma damage
Sponsor
- Bayer HealthCare
Dosage Modifications
Renal impairment
-
CrCl >50 mL/min
- Dose adjustment not necessary
-
CrCl 30-50 mL/min
- Immediate-release: 250-500 mg PO q12hr
- Extended-release: 1 g PO q24hr
- Intravenous: 400 mg IV q8-12hr
-
CrCl 5-29 mL/min
- Immediate-release: 250-500 mg PO q18hr
- Extended-release: 500 mg PO q24hr
- Intravenous: 200-400 mg IV q12-24hr
-
Hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis
- Administer after dialysis
- Immediate-release: 250-500 mg PO q24hr
- Extended-release: 500 mg PO q24hr
- Intravenous: 200-400 mg IV q24hr
Dosing Considerations
ProQuin XR should be taken with a meal, preferably evening meal
Cipro XR may be taken with or without meal; drink fluids liberally
Susceptible organisms
- Aeromonas hydrophila, Bacillus anthracis, Bacteroides fragilis, Campylobacter jejuni, Citrobacter freundii, Citrobacter diversus, Enterobacter cloacae, Enterococcus faecalis, Escherichia coli, Haemophilus ducreyi, Haemophilus influenzae, Haemophilus parainfluenzae, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Legionella pneumophila, Morganella morganii, Moraxella catarrhalis, certain mycobacteria, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Proteus mirabilis, Providencia spp, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Salmonella typhi, Serratia spp, Shigella spp, methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA), Staphylococcus epidermis, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Vibrio cholerae, Yersinia enterocolitica
- First-line therapy: B anthracis, C freundii, C jejuni, Enterobacter spp, Hafnia alvei, S typhi, Salmonella spp, Shigella spp; no unanimity on others (eg, K pneumoniae, M morganii, V cholerae, Y enterocolitica )
Dosage Forms & Strengths
infusion solution
- 200mg/100mL
- 200mg/20mL
- 400mg/40mL
- 400mg/200mL
oral suspension
- 250mg/5mL
- 500mg/5mL
tablet
- 250mg
- 500mg
- 750mg
tablet, extended release
- 500mg
- 1000mg
Complicated Urinary Tract Infections or Pyelonephritis
<1 year: Safety and efficacy not established
≥1 year (IV): 6-10 mg/kg q8hr; individual dose not to exceed 400 mg for 10-21 days
≥1 year (PO): 10-20 mg/kg q12hr; individual dose not to exceed 750 mg q12hr for 10-21 days
Cholera
Multiple doses: 30 mg/kg/day PO divided q12hr for 3 days
Plague
Indication for treatment and prophylaxis of plague due to Yersinia pestis in pediatric patients from birth to 17 years of age
15 mg/kg PO q8-12hr x10-21 days; not to exceed 500 mg/dose, OR
10 mg/kg IV q8-12hr x 10-21 days; not to exceed 400 mg/dose
Inhalational Anthrax (Off-label)
Postexposure therapy
IV: 10 mg/kg q12hr for 60 days; individual dose not to exceed 400 mg
PO: 15 mg/kg q12hr for 60 days; individual dose not to exceed 500 mg
Change antibiotic to amoxicillin as soon as penicillin susceptibility confirmed
Cystic Fibrosis (Off-label)
PO: 40 mg/kg/day divided q12hr; not to exceed 2 g/day
IV: 20-30 mg/kg/day divided q8-12hr; not to exceed 1.2 g/day
Interactions
Interaction Checker
No Results

Contraindicated
Serious - Use Alternative
Significant - Monitor Closely
Minor

Contraindicated (2)
- fezolinetant
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of fezolinetant by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Contraindicated. Fezolinetant AUC and peak plasma concentration are increased if coadministered with drugs that are weak, moderate, or strong CYP1A2 inhibitors
- flibanserin
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of flibanserin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Coadministration of flibanserin with moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors is contraindicated. Severe hypotension or syncope can occur.
Serious - Use Alternative (74)
- alosetron
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of alosetron by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Alosetron is associated with potentially serious and life-threatening, dose-related gastrointestinal adverse effects, concomitant use with CYP450 1A2 inhibitors should generally be avoided if possible.
- aluminum hydroxide
aluminum hydroxide decreases levels of ciprofloxacin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Separate by 2 hours.
- aminolevulinic acid oral
aminolevulinic acid oral, ciprofloxacin. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid administering other phototoxic drugs with aminolevulinic acid oral for 24 hr during perioperative period.
- aminolevulinic acid topical
ciprofloxacin increases toxicity of aminolevulinic acid topical by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of photosensitizing drugs may enhance the phototoxic reaction to photodynamic therapy with aminolevulinic acid.
- amisulpride
amisulpride and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. ECG monitoring is recommended if coadministered.
- anagrelide
anagrelide and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- BCG vaccine live
ciprofloxacin decreases effects of BCG vaccine live by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Antibiotics may diminish therapeutic effects of BCG. Wait until Abx Tx complete to administer live bacterial vaccine.
- buprenorphine
buprenorphine and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- buprenorphine buccal
buprenorphine buccal and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- buprenorphine subdermal implant
buprenorphine subdermal implant and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- buprenorphine transdermal
buprenorphine transdermal and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- buprenorphine, long-acting injection
buprenorphine, long-acting injection and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- carbonyl iron
carbonyl iron decreases levels of ciprofloxacin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ceritinib
ceritinib and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- cholera vaccine
ciprofloxacin, cholera vaccine. pharmacodynamic antagonism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of cholera vaccine with systemic antibiotics since these agents may be active against the vaccine strain. Do not administer cholera vaccine to patients who have received oral or parenteral antibiotics within 14 days prior to vaccination.
- clarithromycin
clarithromycin and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- clomipramine
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of clomipramine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concurrent use of drugs that can cause QT interval prolongation may result in additive effects and increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias. It is important to monitor therapy carefully.
- clozapine
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of clozapine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Use caution when administering ciprofloxacin in patients receiving drugs that prolong the QT interval. At elevated serum concentrations, clozapine may produce clinically significant prolongation of the QTc interval.
clozapine and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - cobimetinib
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of cobimetinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If concurrent short term (14 days or less) use of moderate CYP3A inhibitors is unavoidable for patients who are taking cobimetinib 60 mg, reduce the cobimetinib dose to 20 mg. After discontinuation of a moderate CYP3A inhibitor, resume cobimetinib 60 mg. Use an alternative to a moderate CYP3A inhibitor in patients who are taking a reduced dose of cobimetinib (40 or 20 mg daily).
- desflurane
desflurane and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- didanosine
didanosine decreases levels of ciprofloxacin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Oral ciprofloxacin should not be administered simultaneously with didanosine (chewable tablets or powder for oral solution). Administer oral doses of ciprofloxacin 2 hours before or 6 hours after didanosine, chewable tablets or powder for oral solution.
- dofetilide
dofetilide increases toxicity of ciprofloxacin by QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- dronedarone
ciprofloxacin and dronedarone both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. The use of dronedarone in combination with other medications that can prolong the QT interval is contraindicated.
- eliglustat
eliglustat and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- encorafenib
encorafenib and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- entrectinib
ciprofloxacin and entrectinib both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- eribulin
eribulin and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- fexinidazole
fexinidazole and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of fexinidazole with drugs known to block potassium channels and/or prolong QT interval.
- givinostat
ciprofloxacin and givinostat both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If unable to avoid coadministration, obtain ECGs when initiating, during concomitant use, and as clinically indicated. Withhold if QTc interval >500 ms or a change from baseline >60 ms.
- glasdegib
ciprofloxacin and glasdegib both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration unavoidable, monitor for increased risk of QTc interval prolongation.
- hydroxychloroquine sulfate
hydroxychloroquine sulfate and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ibrutinib
ciprofloxacin increases levels of ibrutinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid concomitant use of ibrutinib and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. If a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor must be used short-term (eg, anti-infectives for =7 days), interrupt ibrutinib therapy until strong CYP3A4 inhibitor is discontinued.
- imipramine
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of imipramine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concurrent use of drugs that can cause QT interval prolongation may result in additive effects and increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias. It is important to monitor therapy carefully.
- inotuzumab
inotuzumab and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If unable to avoid concomitant use, obtain ECGs and electrolytes before and after initiation of any drug known to prolong QTc, and periodically monitor as clinically indicated during treatment.
- iron sucrose
iron sucrose decreases levels of ciprofloxacin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of ciprofloxacin with multivalent cation-containing products may reduce the bioavailability of ciprofloxacin by 90%. Administer ciprofloxacin at least 2 hours before or 6 hours after using these products. Use alternatives if available.
- isoflurane
isoflurane and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ivosidenib
ivosidenib and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of QTc prolonging drugs with ivosidenib or replace with alternate therapies. If coadministration of a QTc prolonging drug is unavoidable, monitor for increased risk of QTc interval prolongation.
- lasmiditan
lasmiditan increases levels of ciprofloxacin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- lefamulin
lefamulin and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- lonafarnib
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of lonafarnib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration of lonafarnib (a sensitive CYP3A substrate) with weak CYP3A inhibitors is unavoidable, reduce to, or continue lonafarnib at starting dose. Closely monitor for arrhythmias and events (eg, syncope, heart palpitations) since lonafarnib effect on QT interval is unknown.
- macimorelin
macimorelin and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Macimorelin causes an increase of ~11 msec in the corrected QT interval. Avoid coadministration with drugs that prolong QT interval, which could increase risk for developing torsade de pointes-type ventricular tachycardia. Allow sufficient washout time of drugs that are known to prolong the QT interval before administering macimorelin.
- mefloquine
mefloquine increases toxicity of ciprofloxacin by QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Mefloquine may enhance the QTc prolonging effect of high risk QTc prolonging agents.
- methyl aminolevulinate
ciprofloxacin, methyl aminolevulinate. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Each drug may increase the photosensitizing effect of the other.
- microbiota oral
ciprofloxacin decreases effects of microbiota oral by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Microbiota oral contains bacterial spores. Antibacterial agents may decrease efficacy if coadministered. Complete antibiotic regimens 2-4 days before initiating microbiota oral. .
- mirtazapine
mirtazapine and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- mobocertinib
mobocertinib and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration unavoidable, reduce mobocertinib dose and monitor QTc interval more frequently.
- olanzapine
olanzapine and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- olaparib
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of olaparib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration with moderate CYP3A inhibitors cannot be avoided, reduce olaparib dose to 200 mg (capsule) or 150 mg (tablet) PO BID. Do not substitute tablets with capsules.
- ondansetron
ciprofloxacin and ondansetron both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid with congenital long QT syndrome; ECG monitoring recommended with concomitant medications that prolong QT interval, electrolyte abnormalities, CHF, or bradyarrhythmias.
- oxaliplatin
oxaliplatin and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- panobinostat
ciprofloxacin and panobinostat both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Panobinostat is known to significantly prolong QT interval. Panobinostat prescribing information states use with drugs known to prolong QTc is not recommended.
- pirfenidone
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of pirfenidone by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Use of strong CYP1A2 inhibitors should be discontinued before initiating pirfenidone and avoided during treatment; if strong CYP1A2 inhibitors are the only drug of choice, dosage reductions are recommended
- pitolisant
ciprofloxacin and pitolisant both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- pomalidomide
ciprofloxacin increases levels of pomalidomide by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- rasagiline
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of rasagiline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Ciprofloxacin may increase rasagiline concentration resulting in increased adverse reactions. Patients should be closely monitored during concomitant use of these drugs.
- ribociclib
ribociclib increases toxicity of ciprofloxacin by QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- saquinavir
saquinavir increases levels of ciprofloxacin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Potential for increased toxicity. Increased risk of QT prolongation and cardiac arrhythmias.
- selinexor
selinexor, ciprofloxacin. unspecified interaction mechanism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Patients treated with selinexor may experience neurological toxicities. Avoid taking selinexor with other medications that may cause dizziness or confusion.
- sevoflurane
sevoflurane and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- siponimod
siponimod and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- sotorasib
sotorasib will decrease the level or effect of ciprofloxacin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If use is unavoidable, refer to the prescribing information of the P-gp substrate for dosage modifications.
- tepotinib
tepotinib will increase the level or effect of ciprofloxacin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If concomitant use unavoidable, reduce the P-gp substrate dosage if recommended in its approved product labeling.
- theophylline
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of theophylline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concomitant use of theophylline and ciprofloxacin has decreased theophylline clearance and increased plasma levels and symptoms of toxicity. Serious and fatal reactions have included cardiac arrest, seizure, status epilepticus, and respiratory failure. If concomitant use cannot be avoided, monitor theophylline levels and adjust dosage as needed.
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of theophylline by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concomitant use of theophylline and ciprofloxacin has decreased theophylline clearance and increased plasma levels and symptoms of toxicity. Serious and fatal reactions have included cardiac arrest, seizure, status epilepticus, and respiratory failure. If concomitant use cannot be avoided, monitor theophylline levels and adjust dosage as needed. - tizanidine
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of tizanidine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of ciprofloxacin and tizanidine is contraindicated.
- toremifene
ciprofloxacin and toremifene both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concurrent use of toremifene with agents causing QT prolongation should be avoided. If concomitant use is required it's recommended that toremifene be interrupted. If interruption not possible, patients requiring therapy with a drug that prolongs QT should be closely monitored. ECGs should be obtained for high risk patients.
- tretinoin
ciprofloxacin, tretinoin. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Both drugs have increased risk of phototoxicity, use caution with concomitant use.
- tretinoin topical
ciprofloxacin, tretinoin topical. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Both drugs have increased risk of phototoxicity, use caution with concomitant use.
- trilaciclib
trilaciclib will decrease the level or effect of ciprofloxacin by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of trilaciclib (OCT2, MATE1, and MATE-2K inhibitor) with substrates where minimal increased concentration in kidney or blood may lead to serious or life-threatening toxicities.
- typhoid vaccine live
ciprofloxacin decreases effects of typhoid vaccine live by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Antibiotics may diminish the therapeutic effects of Typhoid Vaccine. Wait until Abx Tx complete to administer live bacterial vaccine.
- umeclidinium bromide/vilanterol inhaled
ciprofloxacin increases toxicity of umeclidinium bromide/vilanterol inhaled by QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Exercise extreme caution when vilanterol coadministered with drugs that prolong QTc interval; adrenergic agonist effects on the cardiovascular system may be potentiated.
- vandetanib
ciprofloxacin, vandetanib. Either increases toxicity of the other by QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration with drugs known to prolong QT interval; if a drug known to prolong QT interval must be used, more frequent ECG monitoring is recommended.
- vemurafenib
vemurafenib and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concomitant use of vemurafenib with drugs that prolong QT interval is not recommended.
- venetoclax
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of venetoclax by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If a moderate CYP3A inhibitor must be used, reduce the venetoclax dose by at least 50%. Monitor more closely for signs of venetoclax toxicities.
- vilanterol/fluticasone furoate inhaled
ciprofloxacin increases toxicity of vilanterol/fluticasone furoate inhaled by QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Exercise extreme caution when vilanterol coadministered with drugs that prolong QTc interval; adrenergic agonist effects on the cardiovascular system may be potentiated.
Monitor Closely (242)
- acarbose
ciprofloxacin increases effects of acarbose by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Quinolone antibiotic administration may result in hyper- or hypoglycemia. .
- albuterol
albuterol and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- alfuzosin
ciprofloxacin and alfuzosin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
alfuzosin and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - amifampridine
ciprofloxacin increases toxicity of amifampridine by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Comment: Amifampridine can cause seizures. Coadministration with drugs that lower seizure threshold may increase this risk.
- amiodarone
ciprofloxacin and amiodarone both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin elicits minimal effects on QT interval. Caution if used in combination with other drugs known to affect QT interval or in patients with other risk factors.
- arformoterol
arformoterol and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- aripiprazole
aripiprazole and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- arsenic trioxide
ciprofloxacin and arsenic trioxide both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin elicits minimal effects on QT interval. Caution if used in combination with other drugs known to affect QT interval or in patients with other risk factors.
- artemether
ciprofloxacin and artemether both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin elicits minimal effects on QT interval. Caution if used in combination with other drugs known to affect QT interval or in patients with other risk factors.
- artemether/lumefantrine
ciprofloxacin and artemether/lumefantrine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin elicits minimal effects on QT interval. Caution if used in combination with other drugs known to affect QT interval or in patients with other risk factors.
- asenapine
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of asenapine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Asenapine has been associated with dose-related prolongation of the QT interval; asenapine should not be used with other agents also known to have this effect.
ciprofloxacin and asenapine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin elicits minimal effects on QT interval. Caution if used in combination with other drugs known to affect QT interval or in patients with other risk factors. - asenapine transdermal
asenapine transdermal and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- aspirin
aspirin decreases levels of ciprofloxacin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Buffered aspirin may decrease absorption of quinolones. Consider administering 2 hr before or 6 hr after, buffered aspirin administration.
- aspirin/citric acid/sodium bicarbonate
aspirin/citric acid/sodium bicarbonate decreases levels of ciprofloxacin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Buffered aspirin may decrease absorption of quinolones. Consider administering 2 hr before or 6 hr after, buffered aspirin administration.
- atogepant
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of atogepant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- atomoxetine
atomoxetine and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- avapritinib
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of avapritinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- axitinib
ciprofloxacin increases levels of axitinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- azithromycin
azithromycin increases toxicity of ciprofloxacin by QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- bazedoxifene/conjugated estrogens
ciprofloxacin will decrease the level or effect of bazedoxifene/conjugated estrogens by altering intestinal flora. Applies only to oral forms of hormone. Low risk of contraceptive failure. Use Caution/Monitor.
- bedaquiline
ciprofloxacin and bedaquiline both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. ECG should be monitored closely
- benazepril
benazepril increases toxicity of ciprofloxacin by unknown mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. ACE Inhibitors may increase arrhythmogenic potential of ciprofloxacin, possibly by increasing serum potassium levels.
- bendamustine
ciprofloxacin increases levels of bendamustine by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Decreased conversion of bendamustine to active metabolites. Concurrent administration of a CYP1A2 inhibitor such as ciprofloxacin may increase bendamustine concentrations. .
- berotralstat
berotralstat will increase the level or effect of ciprofloxacin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor or titrate P-gp substrate dose if coadministered.
- betamethasone
betamethasone, ciprofloxacin. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Coadministration of quinolone antibiotics and corticosteroids may increase risk of tendon rupture.
- betaxolol
ciprofloxacin increases levels of betaxolol by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Consider modifying therapy; CYP1A2 inhibitors may decrease metabolism of 1A2 substrates.
- biotin
biotin will decrease the level or effect of ciprofloxacin by altering intestinal flora. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor. Administer ciprofloxacin 4 hours before or 2 hours after biotin.
- bosutinib
bosutinib increases levels of ciprofloxacin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- caffeine
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of caffeine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. The hepatic metabolism of caffeine may be decreased by ciprofloxacin; pharmacologic effects of caffeine may be increased.
- calcium acetate
calcium acetate decreases effects of ciprofloxacin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin should be administered 2 hr before or 6 hr after calcium salts.
- calcium carbonate
calcium carbonate decreases effects of ciprofloxacin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin should be administered 2 hr before or 6 hr after calcium salts.
- calcium chloride
calcium chloride decreases effects of ciprofloxacin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin should be administered 2 hr before or 6 hr after calcium salts.
- calcium citrate
calcium citrate decreases effects of ciprofloxacin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin should be administered 2 hr before or 6 hr after calcium salts.
- calcium gluconate
calcium gluconate decreases effects of ciprofloxacin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin should be administered 2 hr before or 6 hr after calcium salts.
- captopril
captopril increases toxicity of ciprofloxacin by Mechanism: unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. ACE Inhibitors increase arrhythmogenic potential of ciprofloxacin. Monitor ECG and QT interval.
- carbamazepine
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by decreasing metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly
- celecoxib
ciprofloxacin, celecoxib. Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Comment: Mechanism: unknown. Increased risk of CNS stimulation and seizures with high doses of fluoroquinolones.
- chloroquine
chloroquine and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin elicits minimal effects on QT interval. Caution if used in combination with other drugs known to affect QT interval or in patients with other risk factors.
- chlorpromazine
ciprofloxacin and chlorpromazine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin elicits minimal effects on QT interval. Caution if used in combination with other drugs known to affect QT interval or in patients with other risk factors.
- chlorpropamide
ciprofloxacin increases effects of chlorpropamide by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Careful monitoring of blood glucose is recommended when quinolones and antidiabetic agents are coadministered. Hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia have been reported in patients treated concomitantly with quinolones and antidiabetic agent.
- citalopram
ciprofloxacin and citalopram both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. ECG monitoring is recommended, along with drugs that may prolong the QT interval.
- colchicine
ciprofloxacin increases toxicity of colchicine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Fatal drug interactions reported when colchicine administered with dual inhibitor of CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein; toxicities also reported when colchicine administered with inhibitors of CYP3A4; coadminister only if no other option available; contraindicated in renal or hepatic impairment with drugs that inhibit both P-gp and CYP3A4.
- conjugated estrogens
ciprofloxacin will decrease the level or effect of conjugated estrogens by altering intestinal flora. Applies only to oral forms of hormone. Low risk of contraceptive failure. Use Caution/Monitor.
- corticotropin
corticotropin and ciprofloxacin both increase Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of quinolone antibiotics and corticosteroids may increase risk of tendon rupture.
- cortisone
cortisone and ciprofloxacin both increase Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of quinolone antibiotics and corticosteroids may increase risk of tendon rupture.
- crizotinib
crizotinib and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. ECG monitoring is recommended, along with drugs that may prolong the QT interval.
- danicopan
danicopan will increase the level or effect of ciprofloxacin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Danicopan increases plasma concentrations of P-gp substrates; consider dose reduction of P-gp substrates where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious adverse reactions.
- dasatinib
dasatinib and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- degarelix
ciprofloxacin and degarelix both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin elicits minimal effects on QT interval. Caution if used in combination with other drugs known to affect QT interval or in patients with other risk factors.
- deutetrabenazine
deutetrabenazine and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. At the maximum recommended dose, deutetrabenazine does not prolong QT interval to a clinically relevant extent. Certain circumstances may increase risk of torsade de pointes and/or sudden death in association with drugs that prolong the QTc interval (eg, bradycardia, hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia, coadministration with other drugs that prolong QTc interval, presence of congenital QT prolongation).
- dexamethasone
dexamethasone and ciprofloxacin both increase Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of quinolone antibiotics and corticosteroids may increase risk of tendon rupture.
- dichlorphenamide
dichlorphenamide and ciprofloxacin both decrease serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- diclofenac
diclofenac, ciprofloxacin. Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Comment: Mechanism: unknown. Increased risk of CNS stimulation and seizures with high doses of fluoroquinolones.
- dienogest/estradiol valerate
ciprofloxacin will decrease the level or effect of dienogest/estradiol valerate by altering intestinal flora. Applies only to oral forms of hormone. Low risk of contraceptive failure. Use Caution/Monitor. An alternate or additional form of birth control may be advisable during concomitant use.
- diflunisal
diflunisal, ciprofloxacin. Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Comment: Mechanism: unknown. Increased risk of CNS stimulation and seizures with high doses of fluoroquinolones.
- disopyramide
ciprofloxacin and disopyramide both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin elicits minimal effects on QT interval. Caution if used in combination with other drugs known to affect QT interval or in patients with other risk factors.
- dofetilide
ciprofloxacin and dofetilide both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin elicits minimal effects on QT interval. Caution if used in combination with other drugs known to affect QT interval or in patients with other risk factors.
- dolasetron
ciprofloxacin and dolasetron both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin elicits minimal effects on QT interval. Caution if used in combination with other drugs known to affect QT interval or in patients with other risk factors.
- donepezil
donepezil and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- doxepin
doxepin and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- droperidol
ciprofloxacin and droperidol both decrease QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin elicits minimal effects on QT interval. Caution if used in combination with other drugs known to affect QT interval or in patients with other risk factors.
- duloxetine
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of CYP1A2 inhibiting quinolones with duloxetine may lead to significant increases in duloxetine levels, AUC, and half-life. Consider therapy modification if duloxetine is necessary.
- efavirenz
efavirenz and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- elagolix
elagolix will increase the level or effect of ciprofloxacin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- eliglustat
eliglustat increases levels of ciprofloxacin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Monitor therapeutic drug concentrations, as indicated, or consider reducing the dosage of the P-gp substrate and titrate to clinical effect.
- eltrombopag
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of eltrombopag by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- eluxadoline
ciprofloxacin increases levels of eluxadoline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. As a precautionary measure due to incomplete information on the metabolism of eluxadoline, use caution when coadministered with strong CYP1A2 inhibitors.
- erlotinib
ciprofloxacin increases levels of erlotinib by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. If severe adverse effects occur consider reducing erlotinib dose.
- erythromycin base
ciprofloxacin and erythromycin base both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of ciprofloxacin with drugs known to prolong QT interval could increase risk of developing torsade de pointes in predisposed patients; however less likely with ciprofloxacin than other quinolones.
- erythromycin ethylsuccinate
ciprofloxacin and erythromycin ethylsuccinate both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of ciprofloxacin with drugs known to prolong QT interval could increase risk of developing torsade de pointes in predisposed patients; however less likely with ciprofloxacin than other quinolones.
- erythromycin lactobionate
ciprofloxacin and erythromycin lactobionate both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of ciprofloxacin with drugs known to prolong QT interval could increase risk of developing torsade de pointes in predisposed patients; however less likely with ciprofloxacin than other quinolones.
- erythromycin stearate
ciprofloxacin and erythromycin stearate both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of ciprofloxacin with drugs known to prolong QT interval could increase risk of developing torsade de pointes in predisposed patients; however less likely with ciprofloxacin than other quinolones.
- escitalopram
escitalopram increases toxicity of ciprofloxacin by QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- estradiol
ciprofloxacin will decrease the level or effect of estradiol by altering intestinal flora. Applies only to oral forms of hormone. Low risk of contraceptive failure. Use Caution/Monitor.
- estrogens conjugated synthetic
ciprofloxacin will decrease the level or effect of estrogens conjugated synthetic by altering intestinal flora. Applies only to oral forms of hormone. Low risk of contraceptive failure. Use Caution/Monitor.
- estropipate
ciprofloxacin will decrease the level or effect of estropipate by altering intestinal flora. Applies only to oral forms of hormone. Low risk of contraceptive failure. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ethinylestradiol
ciprofloxacin will decrease the level or effect of ethinylestradiol by altering intestinal flora. Applies only to oral forms of hormone. Low risk of contraceptive failure. Use Caution/Monitor.
- etodolac
etodolac, ciprofloxacin. Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Comment: Mechanism: unknown. Increased risk of CNS stimulation and seizures with high doses of fluoroquinolones.
- etrasimod
etrasimod, ciprofloxacin. Either increases effects of the other by QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Transient decrease in heart rate and AV conduction delays may occur when initiating etrasimod. Owing to potential of additive effect on heart rate, etrasimod may increase risk of QT prolongation and Torsades de Pointes when coadministered with Class Ia or Class III antiarrhythmic drugs, or other drugs that prolong the QT interval. .
- ezogabine
ezogabine, ciprofloxacin. Either increases toxicity of the other by QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Slight and transient QT-prolongation observed with ezogabine, particularly when dose titrated to 1200 mg/day. QT interval should be monitored when ezogabine is prescribed with agents known to increase QT interval.
- fenoprofen
fenoprofen, ciprofloxacin. Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Comment: Mechanism: unknown. Increased risk of CNS stimulation and seizures with high doses of fluoroquinolones.
- ferric citrate
ferric citrate will decrease the level or effect of ciprofloxacin by drug binding in GI tract. Use Caution/Monitor. Take at least 2 hours before or after ferric citrate
- ferric maltol
ferric maltol decreases effects of ciprofloxacin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of ciprofloxacin with multivalent cation-containing products may reduce the bioavailability of ciprofloxacin by 90%. Administer ciprofloxacin at least 2 hours before or 6 hours after using these products. Use alternatives if available.
- ferrous fumarate
ferrous fumarate decreases levels of ciprofloxacin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of ciprofloxacin with multivalent cation-containing products may reduce the bioavailability of ciprofloxacin by 90%. Administer ciprofloxacin at least 2 hours before or 6 hours after using these products. Use alternatives if available.
- ferrous gluconate
ferrous gluconate decreases levels of ciprofloxacin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of ciprofloxacin with multivalent cation-containing products may reduce the bioavailability of ciprofloxacin by 90%. Administer ciprofloxacin at least 2 hours before or 6 hours after using these products. Use alternatives if available.
- ferrous sulfate
ferrous sulfate decreases effects of ciprofloxacin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of ciprofloxacin with multivalent cation-containing products may reduce the bioavailability of ciprofloxacin by 90%. Administer ciprofloxacin at least 2 hours before or 6 hours after using these products. Use alternatives if available.
- finerenone
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of finerenone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Monitor serum potassium during initiation and dosage adjustment of either finererone or weak CYP3A4 inhibitors. Adjust finererone dosage as needed.
- fingolimod
fingolimod and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- flecainide
ciprofloxacin and flecainide both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin elicits minimal effects on QT interval. Caution if used in combination with other drugs known to affect QT interval or in patients with other risk factors.
- fludrocortisone
fludrocortisone and ciprofloxacin both increase Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of quinolone antibiotics and corticosteroids may increase risk of tendon rupture.
- fluoxetine
ciprofloxacin and fluoxetine both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- flurbiprofen
flurbiprofen, ciprofloxacin. Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Comment: Mechanism: unknown. Increased risk of CNS stimulation and seizures with high doses of fluoroquinolones.
- fostamatinib
fostamatinib will increase the level or effect of ciprofloxacin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant use of fostamatinib may increase concentrations of P-gp substrates. Monitor for toxicities of the P-gp substrate drug that may require dosage reduction when given concurrently with fostamatinib.
- fostemsavir
ciprofloxacin and fostemsavir both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. QTc prolongation reported with higher than recommended doses of fostemsavir.
- gemtuzumab
ciprofloxacin and gemtuzumab both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- gepirone
gepirone and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- gilteritinib
gilteritinib and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- glecaprevir/pibrentasvir
glecaprevir/pibrentasvir will increase the level or effect of ciprofloxacin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- glimepiride
ciprofloxacin increases effects of glimepiride by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Hyper and hypoglycemia have been reported in patients treated concomitantly with quinolones and antidiabetic agents. Careful monitoring of blood glucose is recommended.
- glipizide
ciprofloxacin increases effects of glipizide by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Hyper and hypoglycemia have been reported in patients treated concomitantly with quinolones and antidiabetic agents. Careful monitoring of blood glucose is recommended.
- glyburide
ciprofloxacin increases effects of glyburide by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Hyper and hypoglycemia have been reported in patients treated concomitantly with quinolones and antidiabetic agents. Careful monitoring of blood glucose is recommended.
- goserelin
goserelin increases toxicity of ciprofloxacin by QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Increases risk of torsades de pointes.
- granisetron
granisetron and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- haloperidol
ciprofloxacin and haloperidol both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin elicits minimal effects on QT interval. Caution if used in combination with other drugs known to affect QT interval or in patients with other risk factors.
- histrelin
histrelin increases toxicity of ciprofloxacin by QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Increases risk of torsades de pointes.
- hydrocortisone
hydrocortisone and ciprofloxacin both increase Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of quinolone antibiotics and corticosteroids may increase risk of tendon rupture.
- hydrocortisone rectal
hydrocortisone rectal and ciprofloxacin both increase Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of quinolone antibiotics and corticosteroids may increase risk of tendon rupture.
- hydroxyzine
hydroxyzine and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ibuprofen
ibuprofen, ciprofloxacin. Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Comment: Mechanism: unknown. Increased risk of CNS stimulation and seizures with high doses of fluoroquinolones.
- ibuprofen IV
ibuprofen IV, ciprofloxacin. Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Comment: Mechanism: unknown. Increased risk of CNS stimulation and seizures with high doses of fluoroquinolones.
- ibutilide
ciprofloxacin and ibutilide both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin elicits minimal effects on QT interval. Caution if used in combination with other drugs known to affect QT interval or in patients with other risk factors.
- ifosfamide
ciprofloxacin will decrease the level or effect of ifosfamide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Use of a CYP3A4 inhibitor may decrease metabolism of ifosfamide, potentially reducing ifosfamide therapeutic effects.
- iloperidone
ciprofloxacin and iloperidone both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin elicits minimal effects on QT interval. Caution if used in combination with other drugs known to affect QT interval or in patients with other risk factors.
- indacaterol, inhaled
indacaterol, inhaled, ciprofloxacin. QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Drugs that are known to prolong the QTc interval may have an increased the risk of ventricular arrhythmias.
- indomethacin
indomethacin, ciprofloxacin. Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Comment: Mechanism: unknown. Increased risk of CNS stimulation and seizures with high doses of fluoroquinolones.
- insulin aspart
ciprofloxacin increases effects of insulin aspart by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Hyper and hypoglycemia have been reported in patients treated concomitantly with quinolones and antidiabetic agents. Careful monitoring of blood glucose is recommended.
- insulin lispro
ciprofloxacin increases effects of insulin lispro by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Hyper and hypoglycemia have been reported in patients treated concomitantly with quinolones and antidiabetic agents. Careful monitoring of blood glucose is recommended.
- insulin regular human
ciprofloxacin increases effects of insulin regular human by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Hyper and hypoglycemia have been reported in patients treated concomitantly with quinolones and antidiabetic agents. Careful monitoring of blood glucose is recommended.
- iron dextran complex
iron dextran complex decreases levels of ciprofloxacin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of ciprofloxacin with multivalent cation-containing products may reduce the bioavailability of ciprofloxacin by 90%. Administer ciprofloxacin at least 2 hours before or 6 hours after using these products. Use alternatives if available.
- isavuconazonium sulfate
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of isavuconazonium sulfate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- istradefylline
istradefylline will increase the level or effect of ciprofloxacin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Istradefylline 40 mg/day increased peak levels and AUC of P-gp substrates in clinical trials. Consider dose reduction of sensitive P-gp substrates.
- itraconazole
itraconazole and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ivacaftor
ivacaftor increases levels of ciprofloxacin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Ivacaftor and its M1 metabolite has the potential to inhibit P-gp; may significantly increase systemic exposure to sensitive P-gp substrates with a narrow therapeutic index.
ciprofloxacin increases levels of ivacaftor by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor when coadministered with weak CYP3A4 inhibitors . - ivosidenib
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of ivosidenib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration with moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase ivosidenib plasma concentrations, thus increasing the risk of QTc prolongation. Monitor for increased risk of QTc interval prolongation.
- ketoprofen
ketoprofen, ciprofloxacin. Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Comment: Mechanism: unknown. Increased risk of CNS stimulation and seizures with high doses of fluoroquinolones.
- ketorolac
ketorolac, ciprofloxacin. Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Comment: Mechanism: unknown. Increased risk of CNS stimulation and seizures with high doses of fluoroquinolones.
- lanthanum carbonate
lanthanum carbonate decreases levels of ciprofloxacin by cation binding in GI tract. Use Caution/Monitor. Administer oral quinolone antibiotics at least 1 hr before or 4 hr after lanthanum. Interaction applies only to oral quinolones.
- lemborexant
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of lemborexant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Lower nightly dose of lemborexant recommended if coadministered with weak CYP3A4 inhibitors. See drug monograph for specific dosage modification.
- lenvatinib
ciprofloxacin and lenvatinib both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Lenvatinib prescribing information recommends monitoring ECG closely when coadministered with QT prolonging drugs.
- leuprolide
leuprolide increases toxicity of ciprofloxacin by QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Increases risk of torsades de pointes.
- levonorgestrel oral/ethinylestradiol/ferrous bisglycinate
ciprofloxacin will decrease the level or effect of levonorgestrel oral/ethinylestradiol/ferrous bisglycinate by altering intestinal flora. Applies only to oral forms of hormone. Low risk of contraceptive failure. Use Caution/Monitor. Antibiotics may decrease hormonal contraceptive efficacy.
- lidocaine
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of lidocaine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Lidocaine plasma levels may be elevated, increasing the risk of toxicity. Monitor cardiac function and symptoms of toxicity.
- lithium
lithium and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- lomitapide
ciprofloxacin increases levels of lomitapide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Lomitapide dose should not exceed 30 mg/day.
lomitapide increases levels of ciprofloxacin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider reducing dose when used concomitantly with lomitapide. - lumefantrine
ciprofloxacin and lumefantrine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin elicits minimal effects on QT interval. Caution if used in combination with other drugs known to affect QT interval or in patients with other risk factors.
- magnesium chloride
magnesium chloride decreases levels of ciprofloxacin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of ciprofloxacin with multivalent cation-containing products may reduce the bioavailability of ciprofloxacin by 90%. Administer ciprofloxacin at least 2 hours before or 6 hours after using these products. Use alternatives if available.
- magnesium citrate
magnesium citrate decreases levels of ciprofloxacin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of ciprofloxacin with multivalent cation-containing products may reduce the bioavailability of ciprofloxacin by 90%. Administer ciprofloxacin at least 2 hours before or 6 hours after using these products. Use alternatives if available.
- magnesium hydroxide
magnesium hydroxide decreases levels of ciprofloxacin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of ciprofloxacin with multivalent cation-containing products may reduce the bioavailability of ciprofloxacin by 90%. Administer ciprofloxacin at least 2 hours before or 6 hours after using these products. Use alternatives if available.
- magnesium oxide
magnesium oxide decreases levels of ciprofloxacin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor. Separate by 2 hours.
- magnesium sulfate
magnesium sulfate decreases levels of ciprofloxacin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of ciprofloxacin with multivalent cation-containing products may reduce the bioavailability of ciprofloxacin by 90%. Administer ciprofloxacin at least 2 hours before or 6 hours after using these products. Use alternatives if available.
- magnesium supplement
magnesium supplement will decrease the level or effect of ciprofloxacin by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Formation of an insoluble complex reduces absorption of the drug through intestinal tract; administer magnesium 2hr before the quinolone or 6hr after the quinolone
- meclofenamate
meclofenamate, ciprofloxacin. Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Comment: Mechanism: unknown. Increased risk of CNS stimulation and seizures with high doses of fluoroquinolones.
- mefenamic acid
mefenamic acid, ciprofloxacin. Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Comment: Mechanism: unknown. Increased risk of CNS stimulation and seizures with high doses of fluoroquinolones.
- mefloquine
ciprofloxacin and mefloquine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin elicits minimal effects on QT interval. Caution if used in combination with other drugs known to affect QT interval or in patients with other risk factors.
- melatonin
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of melatonin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor melatonin effects if coadministered with moderate CYP1A2 inhibitors
- meloxicam
meloxicam, ciprofloxacin. Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Comment: Mechanism: unknown. Increased risk of CNS stimulation and seizures with high doses of fluoroquinolones.
- mestranol
ciprofloxacin will decrease the level or effect of mestranol by altering intestinal flora. Applies only to oral forms of hormone. Low risk of contraceptive failure. Use Caution/Monitor.
- metformin
ciprofloxacin increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Hyper and hypoglycemia have been reported in patients treated concomitantly with quinolones and antidiabetic agents. Careful monitoring of blood glucose is recommended.
- methadone
ciprofloxacin and methadone both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin elicits minimal effects on QT interval. Caution if used in combination with other drugs known to affect QT interval or in patients with other risk factors.
- methotrexate
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Renal tubular transport of methotrexate may be inhibited by coadministration of ciprofloxacin, potentially leading to increased methotrexate plasma levels and toxicity.
- methylprednisolone
methylprednisolone and ciprofloxacin both increase Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of quinolone antibiotics and corticosteroids may increase risk of tendon rupture.
- mexiletine
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of mexiletine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Mexiletine concentrations may be elevated and may produce an increase in therapeutic and adverse reactions.
- midazolam intranasal
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of midazolam intranasal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of mild CYP3A4 inhibitors with midazolam intranasal may cause higher midazolam systemic exposure, which may prolong sedation.
- mifepristone
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of mifepristone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Use alternatives if available.
- miglitol
ciprofloxacin increases effects of miglitol by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Hyper and hypoglycemia have been reported in patients treated concomitantly with quinolones and antidiabetic agents. Careful monitoring of blood glucose is recommended.
- mometasone inhaled
mometasone inhaled and ciprofloxacin both increase Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of quinolone antibiotics and corticosteroids may increase risk of tendon rupture.
- moxifloxacin
ciprofloxacin and moxifloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin elicits minimal effects on QT interval. Caution if used in combination with other drugs known to affect QT interval or in patients with other risk factors.
- nabumetone
nabumetone, ciprofloxacin. Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Comment: Mechanism: unknown. Increased risk of CNS stimulation and seizures with high doses of fluoroquinolones.
- naproxen
naproxen, ciprofloxacin. Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Comment: Mechanism: unknown. Increased risk of CNS stimulation and seizures with high doses of fluoroquinolones.
- nateglinide
ciprofloxacin increases effects of nateglinide by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Hyper and hypoglycemia have been reported in patients treated concomitantly with quinolones and antidiabetic agents. Careful monitoring of blood glucose is recommended.
- nilotinib
ciprofloxacin and nilotinib both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin elicits minimal effects on QT interval. Caution if used in combination with other drugs known to affect QT interval or in patients with other risk factors.
- olanzapine
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of olanzapine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Olanzapine plasma concentrations may be elevated, increasing the risk of adverse reactions such as orthostatic hypotension or sedation. It is important to use caution and observe patient and adjust the olanzapine dosage as needed.
- olodaterol inhaled
ciprofloxacin and olodaterol inhaled both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Drugs that prolong the QTc interval and may potentiate the effects of beta2 agonists on the cardiovascular system; increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias
- omeprazole
omeprazole will decrease the level or effect of ciprofloxacin by unknown mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Absorption of the ciprofloxacin ER tablet was slightly diminished (20%) when coadministered with omeprazole.
- osilodrostat
osilodrostat and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- osimertinib
osimertinib and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Conduct periodic monitoring with ECGs and electrolytes in patients taking drugs known to prolong the QTc interval.
- oxaliplatin
oxaliplatin will increase the level or effect of ciprofloxacin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor for ECG changes if therapy is initiated in patients with drugs known to prolong QT interval.
- oxaprozin
oxaprozin, ciprofloxacin. Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Comment: Mechanism unknown. Increased risk of CNS stimulation and seizures with high doses of fluoroquinolones.
- ozanimod
ozanimod and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. The potential additive effects on heart rate, treatment with ozanimod should generally not be initiated in patients who are concurrently treated with QT prolonging drugs with known arrhythmogenic properties.
- paliperidone
ciprofloxacin and paliperidone both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin elicits minimal effects on QT interval. Caution if used in combination with other drugs known to affect QT interval or in patients with other risk factors.
- pasireotide
ciprofloxacin and pasireotide both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- patiromer
patiromer will decrease the level or effect of ciprofloxacin by drug binding in GI tract. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Separate administration by at least 3 hr from patiromer
- pentamidine
ciprofloxacin and pentamidine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin elicits minimal effects on QT interval. Caution if used in combination with other drugs known to affect QT interval or in patients with other risk factors.
- pentoxifylline
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of pentoxifylline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- phenytoin
ciprofloxacin decreases effects of phenytoin by unknown mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin has been reported to both increase and decrease phenytoin concentrations. Additional clinical evidence is needed however; phenytoin serum concentrations should be monitored in patients.
- pimozide
ciprofloxacin and pimozide both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin elicits minimal effects on QT interval. Caution if used in combination with other drugs known to affect QT interval or in patients with other risk factors.
- pioglitazone
ciprofloxacin increases effects of pioglitazone by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Hyper and hypoglycemia have been reported in patients treated concomitantly with quinolones and antidiabetic agents. Careful monitoring of blood glucose is recommended.
- piroxicam
piroxicam, ciprofloxacin. Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Comment: Mechanism: unknown. Increased risk of CNS stimulation and seizures with high doses of fluoroquinolones.
- polysaccharide iron
polysaccharide iron decreases levels of ciprofloxacin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of ciprofloxacin with multivalent cation-containing products may reduce the bioavailability of ciprofloxacin by 90%. Administer ciprofloxacin at least 2 hours before or 6 hours after using these products. Use alternatives if available.
- ponatinib
ponatinib increases levels of ciprofloxacin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- prednisolone
prednisolone and ciprofloxacin both increase Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of quinolone antibiotics and corticosteroids may increase risk of tendon rupture.
- prednisone
prednisone and ciprofloxacin both increase Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of quinolone antibiotics and corticosteroids may increase risk of tendon rupture.
- pretomanid
pretomanid will increase the level or effect of ciprofloxacin by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. In vitro studies demonstrated that pretomanid significantly inhibits OAT3; monitor for increased adverse effects and consider dosage reduction for OAT3 substrates.
- primaquine
primaquine and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- probenecid
probenecid will increase the level or effect of ciprofloxacin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Probenecid interferes with renal tubular secretion of ciprofloxacin and produces an increase in the ciprofloxacin levels in the serum
- procainamide
ciprofloxacin and procainamide both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin elicits minimal effects on QT interval. Caution if used in combination with other drugs known to affect QT interval or in patients with other risk factors.
- quetiapine
quetiapine, ciprofloxacin. Either increases toxicity of the other by QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Avoid use with drugs that prolong QT and in patients with risk factors for prolonged QT interval. Postmarketing cases show QT prolongation with overdose in patients with concomitant illness or with drugs known to cause electrolyte imbalance or prolong QT.
- quinapril
quinapril will decrease the level or effect of ciprofloxacin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Separate doses of quinapril and oral quinolones by 2 hr; interaction likely due to chelation
- quinidine
ciprofloxacin and quinidine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin elicits minimal effects on QT interval. Caution if used in combination with other drugs known to affect QT interval or in patients with other risk factors.
- quinine
ciprofloxacin and quinine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin elicits minimal effects on QT interval. Caution if used in combination with other drugs known to affect QT interval or in patients with other risk factors.
- quizartinib
quizartinib, ciprofloxacin. Either increases effects of the other by QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Monitor patients more frequently with ECG if coadministered with QT prolonging drugs.
- ramelteon
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of ramelteon by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin may decrease the metabolism of ramelteon; if ciprofloxacin is coadministered with ramelteon, monitor the patient closely for toxicity.
- ranolazine
ciprofloxacin and ranolazine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin elicits minimal effects on QT interval. Caution if used in combination with other drugs known to affect QT interval or in patients with other risk factors.
- repaglinide
ciprofloxacin increases effects of repaglinide by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Hyper and hypoglycemia have been reported in patients treated concomitantly with quinolones and antidiabetic agents. Careful monitoring of blood glucose is recommended.
- rilpivirine
rilpivirine increases toxicity of ciprofloxacin by QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Rilpivirine should be used with caution when co-administered with a drug with a known risk of Torsades de Pointes.
- riluzole
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of riluzole by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ropinirole
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of ropinirole by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin may decrease the metabolism of ropinirole; monitor for increased effects of ropinirole.
- ropivacaine
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of ropivacaine by Mechanism: decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor for increased ropivacaine toxicity.
- rosiglitazone
ciprofloxacin increases effects of rosiglitazone by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Hyper and hypoglycemia have been reported in patients treated concomitantly with quinolones and antidiabetic agents. Careful monitoring of blood glucose is recommended.
- saquinavir
ciprofloxacin and saquinavir both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin elicits minimal effects on QT interval. Caution if used in combination with other drugs known to affect QT interval or in patients with other risk factors.
- sarecycline
sarecycline will increase the level or effect of ciprofloxacin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor for toxicities of P-gp substrates that may require dosage reduction when coadministered with P-gp inhibitors.
- saxagliptin
ciprofloxacin increases effects of saxagliptin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Hyper and hypoglycemia have been reported in patients treated concomitantly with quinolones and antidiabetic agents. Careful monitoring of blood glucose is recommended.
- selpercatinib
selpercatinib increases toxicity of ciprofloxacin by QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- sertraline
sertraline and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- sevelamer
sevelamer decreases levels of ciprofloxacin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor. Administer oral quinolones at least 1 hour before or 3 hours after sevelamer. .
- sitagliptin
ciprofloxacin increases effects of sitagliptin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Hyper and hypoglycemia have been reported in patients treated concomitantly with quinolones and antidiabetic agents. Careful monitoring of blood glucose is recommended.
- sodium bicarbonate
sodium bicarbonate decreases levels of ciprofloxacin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor. A large proportion of ciprofloxacin is normally excreted unchanged in the urine. When urinary alkalinizing agents such as sodium bicarbonate are used concomitantly, the solubility of ciprofloxacin can be decreased because of alkaline urine. Patients should be monitored for crystalluria and nephrotoxicity.
- sodium citrate/citric acid
sodium citrate/citric acid decreases levels of ciprofloxacin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor. A large proportion of ciprofloxacin is normally excreted unchanged in the urine. When urinary alkalinizing agents such as sodium citrate are used concomitantly, the solubility of ciprofloxacin can be decreased because of alkaline urine. Patients should be monitored for crystalluria and nephrotoxicity.
- sodium picosulfate/magnesium oxide/anhydrous citric acid
ciprofloxacin decreases effects of sodium picosulfate/magnesium oxide/anhydrous citric acid by altering metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration with antibiotics decreases efficacy by altering colonic bacterial flora needed to convert sodium picosulfate to active drug.
sodium picosulfate/magnesium oxide/anhydrous citric acid decreases levels of ciprofloxacin by cation binding in GI tract. Use Caution/Monitor. Take at least 2 hours before and not less than 6 hours after administration of sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide and anhydrous citric acid to avoid magnesium chelation. - sodium sulfate/?magnesium sulfate/potassium chloride
sodium sulfate/?magnesium sulfate/potassium chloride decreases levels of ciprofloxacin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Administer fluoroquinolones at least 2 hr before and no less than 6 hr after each dose to avoid chelation with magnesium. .
- sodium sulfate/potassium sulfate/magnesium sulfate
sodium sulfate/potassium sulfate/magnesium sulfate decreases levels of ciprofloxacin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Administer fluoroquinolones at least 2 hr before and no less than 6 hr after each dose to avoid chelation with magnesium. .
- solifenacin
solifenacin and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- sorafenib
sorafenib and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- sotalol
ciprofloxacin and sotalol both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin elicits minimal effects on QT interval. Caution if used in combination with other drugs known to affect QT interval or in patients with other risk factors.
- stiripentol
stiripentol will increase the level or effect of ciprofloxacin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider reducing the dose of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) substrates, if adverse reactions are experienced when administered concomitantly with stiripentol.
- sucralfate
sucralfate decreases levels of ciprofloxacin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor. The oral absorption of ciprofloxacin may be significantly reduced by sucralfate secondary to chelation within the GI tract. To help avoid interactions due to chelation, ciprofloxacin should be taken 2 hours before or 6 hours after administration of sucralfate.
- sulindac
sulindac, ciprofloxacin. Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Comment: Mechanism: unknown. Increased risk of CNS stimulation and seizures with high doses of fluoroquinolones.
- sunitinib
ciprofloxacin and sunitinib both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin elicits minimal effects on QT interval. Caution if used in combination with other drugs known to affect QT interval or in patients with other risk factors.
- tacrolimus
tacrolimus and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tasimelteon
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of tasimelteon by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Avoid coadministration; potentially large increase in tasimelteon exposure and greater risk of adverse reactions with strong CYP1A2 inhibitors
- telavancin
ciprofloxacin and telavancin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin elicits minimal effects on QT interval. Caution if used in combination with other drugs known to affect QT interval or in patients with other risk factors.
- terbinafine
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of terbinafine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tetrabenazine
ciprofloxacin and tetrabenazine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin elicits minimal effects on QT interval. Caution if used in combination with other drugs known to affect QT interval or in patients with other risk factors.
- thioridazine
ciprofloxacin and thioridazine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin elicits minimal effects on QT interval. Caution if used in combination with other drugs known to affect QT interval or in patients with other risk factors.
- tinidazole
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of tinidazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tobramycin inhaled
tobramycin inhaled and ciprofloxacin both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Avoid concurrent or sequential use to decrease risk for ototoxicity
- tolazamide
ciprofloxacin increases effects of tolazamide by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Hyper and hypoglycemia have been reported in patients treated concomitantly with quinolones and antidiabetic agents. Careful monitoring of blood glucose is recommended.
- tolbutamide
ciprofloxacin increases effects of tolbutamide by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Hyper and hypoglycemia have been reported in patients treated concomitantly with quinolones and antidiabetic agents. Careful monitoring of blood glucose is recommended.
- tolmetin
tolmetin, ciprofloxacin. Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Comment: Mechanism: unknown. Increased risk of CNS stimulation and seizures with high doses of fluoroquinolones.
- triamcinolone acetonide injectable suspension
triamcinolone acetonide injectable suspension and ciprofloxacin both increase Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of quinolone antibiotics and corticosteroids may increase risk of tendon rupture.
- trimagnesium citrate anhydrous
trimagnesium citrate anhydrous decreases levels of ciprofloxacin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor. Multivalent cation-containing products may reduce bioavailability of quinolones; administer quinolone at least 2 hr before or 6 hr after magnesium; use alternatives if available.
- triptorelin
triptorelin increases toxicity of ciprofloxacin by QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Increases risk of torsades de pointes.
- tucatinib
tucatinib will increase the level or effect of ciprofloxacin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Consider reducing the dosage of P-gp substrates, where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious or life-threatening toxicities.
- vadadustat
vadadustat will increase the level or effect of ciprofloxacin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Vadadustat may increase exposure of OAT3 substrates. Monitor for signs of adverse effect of OAT3 substrate and reduce substrate dose in accordance with their product labeling.
- valbenazine
valbenazine and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- vildagliptin
ciprofloxacin increases effects of vildagliptin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Hyper and hypoglycemia have been reported in patients treated concomitantly with quinolones and antidiabetic agents. Careful monitoring of blood glucose is recommended.
- voclosporin
voclosporin, ciprofloxacin. Either increases effects of the other by QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- vorinostat
vorinostat and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- warfarin
ciprofloxacin increases effects of warfarin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- zinc
zinc will decrease the level or effect of ciprofloxacin by cation binding in GI tract. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Ciprofloxacin should be administered 2 hr before or 6 hr after zinc salts.
- ziprasidone
ciprofloxacin and ziprasidone both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Ciprofloxacin elicits minimal effects on QT interval. Caution if used in combination with other drugs known to affect QT interval or in patients with other risk factors.
- zolpidem
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of zolpidem by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of zolpidem by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
Minor (34)
- acebutolol
ciprofloxacin increases levels of acebutolol by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown. May also rarely decrease beta blocker levels.
- alprazolam
ciprofloxacin increases levels of alprazolam by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- balsalazide
ciprofloxacin will decrease the level or effect of balsalazide by altering intestinal flora. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- carvedilol
ciprofloxacin increases levels of carvedilol by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown. May also rarely decrease beta blocker levels.
- chlordiazepoxide
ciprofloxacin increases levels of chlordiazepoxide by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- clonazepam
ciprofloxacin increases levels of clonazepam by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- clorazepate
ciprofloxacin increases levels of clorazepate by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- diazepam
ciprofloxacin increases levels of diazepam by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- digoxin
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of digoxin by altering intestinal flora. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- esmolol
ciprofloxacin increases levels of esmolol by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- estazolam
ciprofloxacin increases levels of estazolam by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- fennel
fennel decreases levels of ciprofloxacin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Minor/Significance Unknown. Fennel may decrease the amount of ciprofloxacin the body absorbs. Take fennel at least 1 hour after ciprofloxacin administration.
- flurazepam
ciprofloxacin increases levels of flurazepam by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- foscarnet
ciprofloxacin, foscarnet. Mechanism: unknown. Minor/Significance Unknown. Based on 2 case reports it was reported that there is a potential for an increased risk of seizures.
- frovatriptan
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of frovatriptan by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- green tea
ciprofloxacin increases levels of green tea by decreasing elimination. Minor/Significance Unknown. (Caffeine). Some quinolones can inhibit the hepatic clearance of caffeine. Caution is advised.
- isotretinoin
ciprofloxacin, isotretinoin. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Both drugs have increased risk of phototoxicity, use caution with concomitant use.
- metoprolol
ciprofloxacin increases levels of metoprolol by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Ciprofloxacin may increase metoprolol plasma concentrations however mechanism is unknown. Further clinical evidence is needed but it may be appropriate to monitor patients during concomitant therapy with ciprofloxacin.
- midazolam
ciprofloxacin increases levels of midazolam by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- nadolol
ciprofloxacin increases levels of nadolol by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- nebivolol
ciprofloxacin increases levels of nebivolol by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- penbutolol
ciprofloxacin increases levels of penbutolol by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- pindolol
ciprofloxacin increases levels of pindolol by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- propranolol
ciprofloxacin increases levels of propranolol by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- pyridoxine
ciprofloxacin will decrease the level or effect of pyridoxine by altering intestinal flora. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- quazepam
ciprofloxacin increases levels of quazepam by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- quercetin
quercetin decreases effects of ciprofloxacin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ruxolitinib
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of ruxolitinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ruxolitinib topical
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of ruxolitinib topical by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- temazepam
ciprofloxacin increases levels of temazepam by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- thiamine
ciprofloxacin will decrease the level or effect of thiamine by altering intestinal flora. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- timolol
ciprofloxacin increases levels of timolol by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown. May also rarely decrease beta blocker levels.
- triazolam
ciprofloxacin increases levels of triazolam by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- vitamin K1 (phytonadione)
ciprofloxacin will decrease the level or effect of vitamin K1 (phytonadione) by altering intestinal flora. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Minor/Significance Unknown.
Adverse Effects
>10%
Pediatric
- Gastrointestinal (15%)
1-10%
Adults
- Nausea (2.5%)
- Diarrhea (1.6%)
- Liver function tests abnormal (1.3%)
- Vomiting (1%)
- Rash (1%)
Pediatric
- Diarrhea (4.8%)
- Vomiting (4.8%)
- Abdominal pain (3.3%)
- Neurologic (ie, dizziness, nervousness, insomnia, somnolence) (3%)
- Dyspepsia (2.7%)
- Nausea (2.7%)
- Fever (2.1%)
- Asthma (1.8%)
- Rash (1.8%)
<1%
Body as a whole
- Headache
- Abdominal pain/discomfort
- Pain
Cardiovascular
- Syncope
- Angina pectoris
- Myocardial infarction
- Cardiopulmonary arrest
- Tachycardia
- Hypotension
Central nervous system
- Restlessness
- Dizziness
- Insomnia
- Nightmares
- Hallucinations
- Paranoia
- Psychosis (toxic)
- Manic reaction
- Irritability
- Tremor
- Ataxia
- Seizures (including status epilepticus)
- Malaise
- Anorexia
- Phobia
- Depersonalization
- Depression (potentially culminating in self-injurious behavior [eg, suicidal ideations/thoughts and attempted or completed suicide])
- Paresthesia
- Abnormal gait
- Migraine
Gastrointestinal
- Intestinal perforation
- Gastrointestinal bleeding
- Cholestatic jaundice
- Hepatitis
- Pancreatitis
Hemic/lymphatic
- Petechia
Metabolic/nutritional
- Hyperglycemia
- Hypoglycemia
Musculoskeletal
- Arthralgia
- Joint Stiffness
- Muscle Weakness
Renal/urogenital
- Interstitial nephritis
- Renal failure
Respiratory
- Dyspnea
- Laryngeal edema
- Hemoptysis
- Bronchospasm
Skin/hypersensitivity
- Anaphylactic Reactions including life-threatening anaphylactic shock
- Erythema multiforme/Stevens-Johnson
- Syndrome
- Exfoliative dermatitis
- Toxic epidermal necrolysis
- Pruritus
- Urticaria
- Photosensitivity/phototoxicity reaction
- Flushing
- Fever
- Angioedema
- Erythema nodosum
- Sweating
Special senses
- Blurred vision
- Disturbed vision (chromatopsia and photopsia)
- Decreased visual acuity
- Diplopia
- Tinnitus
- Hearing loss
- Bad taste
Postmarketing Reports
Cardiovascular: QT prolongation, Torsade de pointes, vasculitis and ventricular arrhythmia
Central nervous system: Hypertonia, myasthenia, exacerbation of myasthenia gravis, peripheral neuropathy, polyneuropathy, twitching
Eye disorders: Nystagmus
Gastrointestinal: Pseudomembranous colitis
Hemic/lymphatic: Pancytopenia (life threatening or fatal outcome), methemoglobinemia
Hepatobiliary: Hepatic failure (including fatal cases)
Infections and infestations: Candidiasis (oral, gastrointestinal, vaginal)
Investigations: Prothrombin time prolongation or decrease, cholesterol elevation (serum), potassium elevation (serum)
Musculoskeletal: Myalgia, myoclonus, tendinitis, tendon rupture
Psychiatric disorders: Agitation, confusion, delirium
Skin/hypersensitivity: Acute generalize exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), fixed eruption, serum sickness-like reaction
Special senses: Anosmia, hyperesthesia, hypesthesia, taste loss
Warnings
Black Box Warnings
Serious adverse effects
- Fluoroquinolones have been associated with disabling and potentially irreversible serious adverse reactions that have occurred together including: tendinitis and tendon rupture, peripheral neuropathy, and central nervous system (CNS) effects
- Discontinue treatment immediately and avoid use of systemic fluoroquinolones in patients who experience any of these serious adverse reactions
- May exacerbate muscle weakness in patients with myasthenia gravis; avoid fluoroquinolones with known history of myasthenia gravis
Because the risk of these serious side effects generally outweighs the benefits for patients with acute bacterial sinusitis, acute exacerbation of chronic bronchitis, and uncomplicated UTIs, that fluoroquinolones should be reserved for use in patients with these conditions who have no alternative treatment options
Contraindications
Documented hypersensitivity; concurrent tizanidine administration
Cautions
Use in pregnancy, though generally contraindicated for all quinolones, is allowed for life-threatening situations; limited data from use of ciprofloxacin in pregnancy show no higher rate of birth defects than background
Do not use oral suspension in nasogastric tube; to prepare, add microcapsules to diluent
Commonly seen adverse reactions include tendinitis, tendon rupture, arthralgia, myalgia, peripheral neuropathy, and central nervous system effects (hallucinations, anxiety, depression, insomnia, severe headaches, and confusion); these reactions can occur within hours to weeks after starting therapy, including in patients of any age or without pre-existing risk factors; discontinue therapy immediately at first signs or symptoms of any serious adverse reaction; in addition, avoid use of fluoroquinolones, in patients who have experienced any serious adverse reactions associated with fluoroquinolones (see Black Box Warnings)
Peripheral neuropathy: sensory or sensorimotor axonal polyneuropathy affecting small and/or large axons resulting in paresthesias, hypoesthesias, dysesthesias, and weakness reported; peripheral neuropathy may occur rapidly after initiating and may potentially become permanent
In prolonged therapy, perform periodic evaluations of organ system functions (eg, renal, hepatic, hematopoietic); adjust dose in renal impairment; superinfections may occur with prolonged or repeated antibiotic therapy; discontinue use immediately if signs and symptoms of hepatitis occur
Not first drug of choice in pediatrics (except in anthrax), because of increased incidence of adverse events in comparison with control subjects, including arthropathy; no data exist on dosing for pediatric patients with renal impairment (ie, CrCl <50 mL/min)
Crystalluria may occur; urine alkalinity may increase risk; ensure adequate hydration during therapy
Serious and sometimes fatal hypoglycemia reported with fluoroquinolone use; hyperglycemia also reported; monitor patients closely for signs/symptoms of abnormal glucose levels; if hypoglycemic reaction occurs in a patient being treated discontinue therapy and initiate appropriate treatment immediately
Moderate-to-severe phototoxicity reactions reported; avoid excessive sunlight and take precautions to limit exposure; discontinue use if phototoxicity occurs
Acute onset of retinal detachment increased 4.5-fold with oral fluoroquinolones in a single case-controlled study - JAMA 2012;307(13):1414-1419; another study disputes these findings (relative risk, 1.29) - JAMA 2013;310(20):2184-2190
Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD) reported; if CDAD suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibiotic use not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued; appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibiotic treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated
Prescribing antibiotics in absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection or a prophylactic indication is unlikely to provide benefit to patient and increases risk of development of drug-resistant bacteria
Fluoroquinolones may exacerbate muscle weakness in patients with myasthenia gravis; postmarketing serious adverse reactions, including deaths and requirement for ventilatory support, have been associated with fluoroquinolone use in patients with myasthenia gravis; avoid in patients with known history of myasthenia gravis
CNS effects
- Fluoroquinolones are associated with an increased risk of CNS effects(eg, convulsions, increased intracranial pressure [including pseudotumor cerebri], and toxic psychosis)
- May also cause CNS events including: nervousness, agitation, insomnia, anxiety, nightmares, paranoia, dizziness, confusion, tremors, hallucinations, depression, and psychotic reactions have progressed to suicidal ideations/thoughts and self-injurious behavior such as attempted or completed suicide; reactions may occur following the first dose; advise patients to inform their healthcare provider immediately if these reactions occur, discontinue treatment, and institute appropriate care
- Fluoroquinolone are also known to trigger seizures or lower the seizure threshold; exercise caution in epileptic patients and patients with known or suspected CNS disorders that may predispose to seizures or lower the seizure threshold (eg, severe cerebral arteriosclerosis, previous history of convulsion, reduced cerebral blood flow, altered brain structure, stroke), or in the presence of other risk factors that may predispose to seizures or lower the seizure threshold (eg, certain drug therapy, renal dysfunction)
- Cases of status epilepticus have been reported; if seizures occur, discontinue treatment
FDA MedWatch Safety Alert
- Issued 12-20-2018
- Increase in rate of aortic aneurysm and dissection reported within two months following use of fluoroquinolones, particularly in elderly patients
- May occur with fluoroquinolones for systemic use (IV or PO)
- Patients who have an aortic aneurysm or are at risk for an aortic aneurysm (eg, patients with peripheral atherosclerotic vascular diseases, hypertension, certain genetic conditions [eg, Marfan syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome], elderly patients)
- Prescribe fluoroquinolones to these patients only when no other treatment options are available
- Advise patients to seek immediate medical treatment for any symptoms associated with aortic aneurysm
- Stop treatment immediately if a patient reports side effects suggestive of aortic aneurysm or dissection
FDA MedWatch Safety Alert
- Issued July 10, 2018
- The FDA is strengthening the current warnings in the prescribing information for fluoroquinolone antibiotics to inform clinicians of significant decreases in blood glucose and certain mental health adverse effects
- Hypoglycemia, sometimes resulting in coma, occurred more frequently in elderly patients or in diabetic patients taking oral hypoglycemic medicine or insulin
- Alert patients regarding hypoglycemic symptoms and carefully monitor blood glucose levels; instruct patients how to treat themselves if symptoms of hypoglycemia occur
- This safety alert affects only systemic formulations; early signs and symptoms of low blood glucose include confusion, dizziness, feeling shaky, unusual hunger, headaches, irritability, pounding heart or very fast pulse, pale skin, sweating, trembling, weakness, and/or unusual anxiety
- Mental health side effects are to be added to or updated across all the fluoroquinolones are disturbances in attention, disorientation, agitation, nervousness, memory impairment, and delirium
- Inform patients of the potential risk of psychiatric adverse reactions that can occur after just 1 dose
- Immediately discontinue treatment if CNS adverse effects occur, including psychiatric adverse reactions, or blood glucose disturbances occur and switch to a nonfluoroquinolone antibiotic if possible
Drug interactions overview
- Serious and fatal reactions have reported in patients receiving concurrent administration of ciprofloxacin and theophylline; if concomitant use cannot be avoided, monitor serum levels of theophylline and adjust dosage as appropriate
- Coadministration of IV ciprofloxacin and other drugs primarily metabolized by CYP1A2 (for example, theophylline, methylxanthines, caffeine, tizanidine, ropinirole, clozapine, olanzapine, and zolpidem) results in increased plasma concentrations of co-administered drug and could lead to clinically significant pharmacodynamic adverse reactions of the co-administered drug
- Use with caution in patients with history of seizures taking concurrent therapy that lowers seizure threshold; risk increases rarely when administered concomitantly with NSAIDs
- Avoid IV administration in patients who have known QT prolongation, carry risk factors for prolonged QT, or are taking class 1A or class III antiarrhythmic drugs
Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy
Prolonged experience with ciprofloxacin in pregnant women over several decades, based on available published information from case reports, case control studies and observational studies during pregnancy, have not identified any drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes
Oral administration during organogenesis at doses up to 100 mg/kg to pregnant mice and rats, and up to 30 mg/kg to pregnant rabbits did not cause fetal malformations; these doses were up to 0.3, 0.6, and 0.4 times the maximum recommended clinical oral dose in mice, rats, and rabbits, respectively, based on body surface area
Lactation
Published literature reports that ciprofloxacin is present in human milk following intravenous and oral administration; there is no information regarding effects on milk production or breastfed infant; because of potential risk of serious adverse reactions in breastfed infants, including arthropathy shown in juvenile animal studies
For most indications a lactating woman may consider pumping and discarding breast milk during treatment and an additional two days (five half-lives) after last dose; alternatively, advise a woman that breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment and for an additional two days (five half-lives) after last dose
However, for inhalation anthrax (post exposure), during an incident resulting in exposure to anthrax, the risk-benefit assessment of continuing breastfeeding while the mother (and potentially the infant) is (are) on CIPRO may be acceptable
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for therapy and any potential adverse effects on breastfed child from drug or from underlying maternal condition
Ciprofloxacin may cause intestinal flora alteration of breastfeeding infant; advise a woman to monitor breastfed infant for loose or bloody stools and candidiasis (thrush, diaper rash)
Pregnancy Categories
A: Generally acceptable. Controlled studies in pregnant women show no evidence of fetal risk.
B: May be acceptable. Either animal studies show no risk but human studies not available or animal studies showed minor risks and human studies done and showed no risk. C: Use with caution if benefits outweigh risks. Animal studies show risk and human studies not available or neither animal nor human studies done. D: Use in LIFE-THREATENING emergencies when no safer drug available. Positive evidence of human fetal risk. X: Do not use in pregnancy. Risks involved outweigh potential benefits. Safer alternatives exist. NA: Information not available.Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Inhibits relaxation of DNA; inhibits DNA gyrase in susceptible organisms; promotes breakage of double-stranded DNA
Absorption
Bioavailability (PO): ~50-85%
Peak plasma time (PO): Immediate-release, 0.5-2 hr; extended-release, 1-2.5 hr
Distribution
Distributed widely throughout body; tissue concentrations often exceed serum concentrations, especially in kidneys, gallbladder, liver, lungs, gynecologic tissue, and prostatic tissue; cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) concentration is 10% in noninflamed meninges and 14-37% in inflamed meninges; crosses placenta; enters breast milk
Protein bound: 20-40%
Vd: 2.1-2.7 L/kg
Metabolism
Metabolized in liver
Enzyme inhibitor: CYP1A2
Elimination
Half-life: 2-5 hr (children); 3-5 hr (adults)
Excretion: Urine (30-50%), feces (15-43%)
Administration
IV Incompatibilities
Additive: Aminophylline, amoxicillin, amoxicillin-clavulanate, amphotericin, ampicillin-sulbactam, ceftazidime, cefuroxime, clindamycin, floxacillin, heparin, piperacillin, sodium bicarbonate, ticarcillin
Y-site: Aminophylline, ampicillin-sulbactam, azithromycin, cefepime, dexamethasone sodium phosphate, furosemide, heparin, hydrocortisone sodium succinate, magnesium sulfate(?), methylprednisolone sodium succinate, phenytoin, potassium phosphates, propofol, sodium bicarbonate(?), sodium phosphates, total parenteral nutrition formulations, warfarin
IV Compatibilities
Solution: Compatible with most IV fluids
Additive: Amikacin, aztreonam, dobutamine, dopamine, fluconazole, gentamicin, lidocaine, linezolid, metronidazole (ready-to-use form is compatible; hydrochloride form in vial is incompatible), midazolam, potassium chloride, tobramycin
Y-site: Amiodarone, calcium gluconate, clarithromycin, digoxin, diphenhydramine, dobutamine, dopamine, linezolid, lorazepam, midazolam, promethazine, quinupristin/dalfopristin, tacrolimus
IV Administration
Infuse 1-2 mg/mL (diluted in D5W or NS) into large vein over 60 minutes
When administering intermittently through Y-site, temporarily discontinue primary solution
Oral Administration
May take with or without food
Tablet
- If given with food, there is delayed absorption resulting in peak concentrations that occur closer to 2 hr after dosing rather than 1 hr
Oral suspension
- Shake well for 15 seconds before measuring each dose
- No delayed absorption if given with food
Coadministration with multivalent cations or dairy
-
Multivalent cations
- Take ciprofloxacin at least 2 hr before or 6 hr after multivalent cations
- Examples: Magnesium/aluminum antacids, sucralfate, polymeric phosphate binders (eg, sevelamer, lanthanum carbonate), other highly buffered drugs, or other products containing calcium, iron, or zinc
-
Dairy
- Avoid concomitant administration with dairy products (milk or yogurt) or calcium-fortified juices alone since decreased absorption is possible
- However, ciprofloxacin may be taken with a meal that contains these products
Hydration
- Assure adequate hydration of patients to prevent formation of highly concentrated urine
- Crystalluria reported with quinolones
Missed dose
- >6 hr before next dose: Take missed dose
- <6 hr before next dose: Do not take, resume dosing with next schedules dose
- Do not double the dose to compensate for a missed dose
Splitting tablets
- Cipro: 250-mg and 500-mg tablets are functionally scored, which can be split into one-half at the scored line to provide a 125-mg and 250-mg strength, respectively
Stability
IV stable at concentration of 0.5-2 mg/mL in D5W or NS for 14 days at room temperature or refrigerated
Images
| BRAND | FORM. | UNIT PRICE | PILL IMAGE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cipro oral - | 250 mg/5 mL suspension | 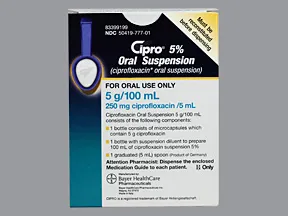 | |
| Cipro oral - | 250 mg tablet |  | |
| Cipro oral - | 500 mg tablet |  | |
| Cipro oral - | 500 mg/5 mL suspension |  | |
| Cipro oral - | 500 mg tablet |  |
Copyright © 2010 First DataBank, Inc.
Patient Handout
Ciprofloxacin
CIPROFLOXACIN SUSPENSION - ORAL
(SIP-roe-FLOX-a-sin)
COMMON BRAND NAME(S): Cipro
WARNING: Quinolone antibiotics (including ciprofloxacin) may cause serious and possibly permanent tendon damage (such as tendonitis, tendon rupture), nerve problems in the arms and legs (peripheral neuropathy), and nervous system problems. Get medical help right away if you have any of the following symptoms: pain/numbness/burning/tingling/weakness in your arms/hands/legs/feet, changes in how you sense touch/pain/temperature/vibration/body position, severe/lasting headache, vision changes, shaking (tremors), seizures, mental/mood changes (such as agitation, anxiety, confusion, hallucinations, depression, rare thoughts of suicide).Tendon damage may occur during or after treatment with this medication. Stop exercising, rest, and get medical help right away if you develop joint/muscle/tendon pain or swelling. Your risk for tendon problems is greater if you are over 60 years of age, if you are taking corticosteroids (such as prednisone), or if you have a kidney, heart, or lung transplant.This medication may make a certain muscle condition (myasthenia gravis) worse. Tell your doctor right away if you have new or worsening muscle weakness (such as drooping eyelids, unsteady walk) or trouble breathing.Discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor before using this medication.
USES: This medication is used to treat a variety of bacterial infections. Ciprofloxacin belongs to a class of drugs called quinolone antibiotics. It works by stopping the growth of bacteria.This antibiotic treats only bacterial infections. It will not work for virus infections (such as common cold, flu). Using any antibiotic when it is not needed can cause it to not work for future infections.
HOW TO USE: Read the Medication Guide and, if available, the Patient Information Leaflet provided by your pharmacist before you start taking ciprofloxacin and each time you get a refill. If you have any questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.This medication may be taken with or without food as directed by your doctor, usually twice a day (every 12 hours).Shake the container well for 15 seconds before pouring each dose. Carefully measure the dose using a special measuring device/spoon. Do not use a household spoon because you may not get the correct dose. Do not chew the contents of the suspension.Do not use the suspension with feeding tubes because the suspension may clog the tube.The dosage and length of treatment is based on your medical condition and response to treatment. Drink plenty of fluids while taking this medication unless your doctor tells you otherwise.Take this medication at least 2 hours before or 6 hours after taking other products that may bind to it, decreasing its effectiveness. Ask your pharmacist about the other products you take. Some examples include: quinapril, sevelamer, sucralfate, vitamins/minerals (including iron and zinc supplements), and products containing magnesium, aluminum, or calcium (such as antacids, didanosine solution, calcium supplements).Calcium-rich foods, including dairy products (such as milk, yogurt) or calcium-enriched juice, can also decrease the effect of this medication. Take this medication at least 2 hours before or 6 hours after eating calcium-rich foods, unless you are eating these foods as part of a larger meal that contains other (non-calcium-rich) foods. These other foods decrease the calcium binding effect.Ask your doctor or pharmacist about safely using nutritional supplements/replacements with this medication.For the best effect, take this antibiotic at evenly spaced times. To help you remember, take this medication at the same time(s) every day.Continue to take this medication until the full prescribed amount is finished, even if symptoms disappear after a few days. Stopping the medication too early may result in a return of the infection.Tell your doctor if your condition lasts or gets worse.
SIDE EFFECTS: See also Warning section.Nausea, diarrhea, dizziness, lightheadedness, headache, or trouble sleeping may occur. If any of these effects last or get worse, tell your doctor or pharmacist promptly.Remember that this medication has been prescribed because your doctor has judged that the benefit to you is greater than the risk of side effects. Many people using this medication do not have serious side effects.Tell your doctor right away if you have any serious side effects, including: unusual bruising/bleeding, signs of a new infection (such as sore throat that doesn't go away, fever), signs of kidney problems (such as change in the amount of urine, red/pink urine), signs of liver problems (such as nausea/vomiting that doesn't stop, unusual tiredness, stomach/abdominal pain, yellowing eyes/skin, dark urine).Get medical help right away if you have any very serious side effects, including: severe dizziness, fainting, fast/irregular heartbeat, signs of a tear/break in the main blood vessel called the aorta (such as sudden/severe pain in the stomach/chest/back, shortness of breath).This medication may rarely cause a severe intestinal condition due to a bacteria called C. difficile. This condition may occur during treatment or weeks to months after treatment has stopped. Tell your doctor right away if you develop: diarrhea that doesn't stop, abdominal or stomach pain/cramping, blood/mucus in your stool.If you have these symptoms, do not use anti-diarrhea or opioid products because they may make symptoms worse.Use of this medication for prolonged or repeated periods may result in oral thrush or a new yeast infection. Contact your doctor if you notice white patches in your mouth, a change in vaginal discharge, or other new symptoms.A very serious allergic reaction to this drug is rare. However, get medical help right away if you notice any of the following symptoms of a serious allergic reaction: rash, itching/swelling (especially of the face/tongue/throat), severe dizziness, trouble breathing.This is not a complete list of possible side effects. If you notice other effects not listed above, contact your doctor or pharmacist.In the US -Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or at www.fda.gov/medwatch.In Canada - Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to Health Canada at 1-866-234-2345.
PRECAUTIONS: Before taking ciprofloxacin, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are allergic to it; or to other quinolone antibiotics such as norfloxacin, gemifloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin, or ofloxacin; or if you have any other allergies. This product may contain inactive ingredients, which can cause allergic reactions or other problems. Talk to your pharmacist for more details.Before using this medication, tell your doctor or pharmacist your medical history, especially of: diabetes, heart problems (such as recent heart attack), joint/tendon problems (such as tendonitis, bursitis), kidney disease, liver disease, mental/mood disorders (such as depression), myasthenia gravis, nerve problems (such as peripheral neuropathy), seizures, conditions that increase your risk of seizures (such as brain/head injury, brain tumors, cerebral atherosclerosis), blood vessel problems (such as aneurysm or blockage of the aorta or other blood vessels, hardening of the arteries), high blood pressure, certain genetic conditions (Marfan syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome).Ciprofloxacin may cause a condition that affects the heart rhythm (QT prolongation). QT prolongation can rarely cause serious (rarely fatal) fast/irregular heartbeat and other symptoms (such as severe dizziness, fainting) that need medical attention right away.The risk of QT prolongation may be increased if you have certain medical conditions or are taking other drugs that may cause QT prolongation. Before using ciprofloxacin, tell your doctor or pharmacist of all the drugs you take and if you have any of the following conditions: certain heart problems (heart failure, slow heartbeat, QT prolongation in the EKG), family history of certain heart problems (QT prolongation in the EKG, sudden cardiac death).Low levels of potassium or magnesium in the blood may also increase your risk of QT prolongation. This risk may increase if you use certain drugs (such as diuretics/"water pills") or if you have conditions such as severe sweating, diarrhea, or vomiting. Talk to your doctor about using ciprofloxacin safely.This medication may rarely cause serious changes in blood sugar, especially if you have diabetes. Check your blood sugar regularly as directed and share the results with your doctor. Watch for symptoms of high blood sugar such as increased thirst/urination. Ciprofloxacin may increase the blood-sugar-lowering effects of the medication glyburide. Also watch for symptoms of low blood sugar such as sudden sweating, shaking, fast heartbeat, hunger, blurred vision, dizziness, or tingling hands/feet. It is a good habit to carry glucose tablets or gel to treat low blood sugar. If you don't have these reliable forms of glucose, rapidly raise your blood sugar by eating a quick source of sugar such as table sugar, honey, or candy, or by drinking fruit juice or non- diet soda. Tell your doctor right away about the reaction and the use of this product. To help prevent low blood sugar, eat meals on a regular schedule, and do not skip meals. Your doctor may need to switch you to another antibiotic or adjust your diabetes medications if any reaction occurs.This drug may make you dizzy. Alcohol or marijuana (cannabis) can make you more dizzy. Do not drive, use machinery, or do anything that needs alertness until you can do it safely. Limit alcoholic beverages. Talk to your doctor if you are using marijuana (cannabis).This medication may make you more sensitive to the sun. Limit your time in the sun. Avoid tanning booths and sunlamps. Use sunscreen and wear protective clothing when outdoors. Tell your doctor right away if you get sunburned or have skin blisters/redness.Ciprofloxacin may cause live bacterial vaccines (such as typhoid vaccine) to not work well. Tell your health care professional that you are using ciprofloxacin before having any immunizations/vaccinations.Before having surgery, tell your doctor or dentist about all the products you use (including prescription drugs, nonprescription drugs, and herbal products).This medication contains sucrose. It is not recommended if you have a rare hereditary metabolic condition (such as fructose intolerance, sucrase-isomaltase deficiency, glucose-galactose malabsorption).Children may be more sensitive to the side effects of this drug, especially joint/tendon problems.Older adults may be at greater risk for tendon problems (especially if they are also taking corticosteroids such as prednisone or hydrocortisone), QT prolongation, and a sudden tear/break in the main blood vessel (aorta).During pregnancy, this medication should be used only when clearly needed. Discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor.This medication passes into breast milk and may have undesirable effects on a nursing infant. Consult your doctor before breastfeeding.
DRUG INTERACTIONS: See also How to Use and Precautions sections.Drug interactions may change how your medications work or increase your risk for serious side effects. This document does not contain all possible drug interactions. Keep a list of all the products you use (including prescription/nonprescription drugs and herbal products) and share it with your doctor and pharmacist. Do not start, stop, or change the dosage of any medicines without your doctor's approval.Some products that may interact with this drug include: "blood thinners" (such as acenocoumarol, warfarin), strontium.Many drugs besides ciprofloxacin may affect the heart rhythm (QT prolongation), including amiodarone, dofetilide, quinidine, procainamide, sotalol, among others.This medication can slow down the removal of other medications from your body, which may affect how they work. Examples of affected drugs include duloxetine, fezolinetant, pirfenidone, tasimelteon, tizanidine, among others.Avoid drinking large amounts of beverages containing caffeine (coffee, tea, colas), eating large amounts of chocolate, or taking over-the-counter products that contain caffeine. This drug may increase and/or prolong the effects of caffeine.
OVERDOSE: If someone has overdosed and has serious symptoms such as passing out or trouble breathing, call 911. Otherwise, call a poison control center right away. US residents can call their local poison control center at 1-800-222-1222. Canada residents can call a provincial poison control center.
NOTES: Do not share this medication with others.This medication has been prescribed for your current condition only. Do not use it later for another infection unless your doctor tells you to.Lab and/or medical tests (such as kidney function, blood counts, cultures) should be done while you are taking this medication. Keep all medical and lab appointments. Consult your doctor for more details.Do not change brands of this medication without asking your doctor or pharmacist. Not all brands have the same effects.
MISSED DOSE: If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it is less than 6 hours before the next dose, skip the missed dose. Take your next dose at the regular time. Do not double the dose to catch up.
STORAGE: Before mixing, store the dry powder and mixing solution in an upright position at room temperature. Do not freeze. Once mixed, store the suspension in an upright position in the refrigerator or at room temperature. Discard any unused suspension 14 days after mixing. Do not freeze. Do not store in the bathroom. Keep all medications away from children and pets.Do not flush medications down the toilet or pour them into a drain unless instructed to do so. Properly discard this product when it is expired or no longer needed. Consult your pharmacist or local waste disposal company.
Information last revised March 2024. Copyright(c) 2024 First Databank, Inc.
IMPORTANT: HOW TO USE THIS INFORMATION: This is a summary and does NOT have all possible information about this product. This information does not assure that this product is safe, effective, or appropriate for you. This information is not individual medical advice and does not substitute for the advice of your health care professional. Always ask your health care professional for complete information about this product and your specific health needs.
Formulary
Adding plans allows you to compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
To view formulary information first create a list of plans. Your list will be saved and can be edited at any time.
Adding plans allows you to:
- View the formulary and any restrictions for each plan.
- Manage and view all your plans together – even plans in different states.
- Compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
- Access your plan list on any device – mobile or desktop.



