Oxygen
Different industries, including health systems, use oxygen in regular basis. Oxygen in the market is available for industrial and medical use. Medical-use oxygen is very different from industrial oxygen in purity and quality. Thus, industrial and medical use are not interchangeable.
"Industrial oxygen is not intended for human use. Solely medicinal oxygen that was tested to meet authorized specifications for its identity, purity and content and that was produced, stored and distributed following appropriate practices should reach the patient. Uncertainties regarding the purity and content of industrial oxygen, the possible occurrence of particulate and microbial contamination, and production, storage and distribution processes that may not be appropriately planned, performed and controlled can result in unacceptable risks for patients."

WHO’s Dr Simon Ssentamu verifies the oxygen cylinder supply at a health facility in Kutupalang refugee camp.
Medical-use oxygen
Depending on the source and production method the medical oxygen has the following values:
- For oxygen produced by the air-liquefaction process, the International Pharmacopoeia, defines the requirements of medical-use oxygen. Currently, oxygen must contains not less than 99.5% v/v of O2.
- For Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA) plants, the WHO interim guidance technical specifications for PSA plants, published in June 2020, specifies: "pressure swing adsorption technology to produce medical oxygen 93%±3 from ambient air"
- For oxygen concentrators, the WHO-UNICEF technical specifications and guidance for oxygen therapy devices, published in 2019, as one of the sources of oxygen. “The concentrator should delivery of low-flow, continuous, clean and concentrated oxygen (> 82%) from room air (21%). “ This same statement was published in WHO interim guidance of WHO list of Priority Medical devices for COVID-19 and its associated technical specifications, published November 2020.
Currently WHO has two open consultations related to medical oxygen. For further detail, visit the Health Products and policy Standards- Working documents in public consultation website. The consultations refer to:
- WHO good manufacturing practices 5 for medicinal gases (QAS/21.875/Rev.1) - closing date 31 August 2021
- Medicinal Oxygen (QAS/20-867/Rev.2) - closing date 10 September 2021
Many levels of the health systems need medical oxygen. The units in the health system that use oxygen include:
- Primary health care
- General wards
- Emergency transport
- Delivery rooms
- Operating theaters
- Intensive care units (ICU)
- Specialized hospitals
- Outpatient units
- Etc.
This diagram illustrates examples of medical units that use oxygen. All levels in the health system require oxygen and pulse oximeters (to monitor oxygen saturation in patients). These different levels and scenarios meet different needs of oxygen systems.

Source: WHO-UNICEF technical specifications and guidance for oxygen therapy devices. Geneva: World Health Organization and the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF), 2019 (WHO medical device technical series). Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO
Despite being an essential medicine, oxygen is a complex product. It needs to be produce by a medical device or Industrial plant. Oxygen also requires a whole system to safely reach patients. Oxygen systems consist of oxygen:
- Sources
- Distribution
- Regulation and conditioning
- Delivery
- Patient monitoring
Oxygen systems need regular power supplies and maintenance to function adequately. The following diagram illustrates all the components of an oxygen system.

Source: WHO-UNICEF technical specifications and guidance for oxygen therapy devices. Geneva: World Health Organization and the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF), 2019 (WHO medical device technical series). Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO
Due to their complexity, access to oxygen meets many challenges on:
- Availability
- Quality
- Affordability
- Management
- Supply
- Human resources capacity
- Safety
In face of these challenges, the WHO continuously develops resources to overcome them. WHO latest efforts include the development of technical specifications. The purpose of technical specifications is to increase access to quality products. It also aims to ensure the supply of oxygen, in low-resource settings. These efforts also aim to support ministries of health by:
- ensuring oxygen supply is available
- highlighting the importance of appropriate selection, procurement, maintenance and use of medical devices.
Publications
All →
Priority medical devices list for the COVID-19 response and associated technical specifications
This document describes the medical devices required for the clinical management of COVID-19, selected and prioritized according to the...

Oxygen is an essential medicine required at all levels of the health care system; only high quality, medical-grade oxygen should be given to patients. ...

Clinical management of COVID-19
This guidance document is intended for clinicians caring for COVID-19 patients during all phases of their disease (i.e. screening to discharge). ...

This interim guidance on oxygen sources and distribution strategies for COVID-19 treatment has been adapted from WHO and UNICEF’s technical specifications...

The purpose of this interagency publication is to provide harmonized product specifications for a wide range of products for delivering basic oxygen therapy,...

Oxygen therapy for children
Hypoxaemia is a major contributor to child deaths that occur worldwide each year; for a child with pneumonia hypoxaemia increases the risk of death by...

WHO technical specifications for oxygen concentrators
The purpose of this guidance document is for the appropriate selection, procurement, utilization and maintenance of oxygen concentrators. This document...
Documents
Risk mitigation when using medical oxygen



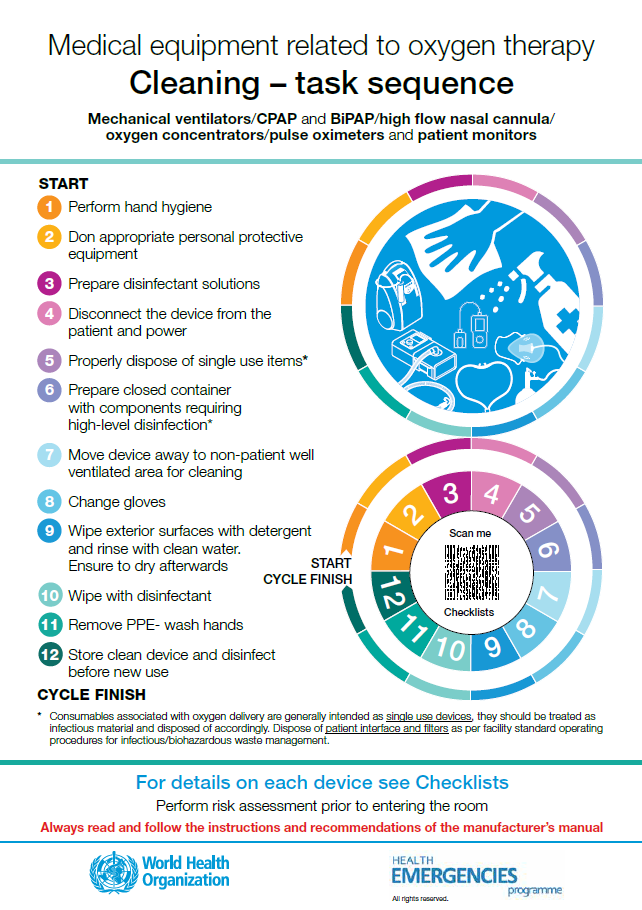
Medical equipment related to oxygen therapy
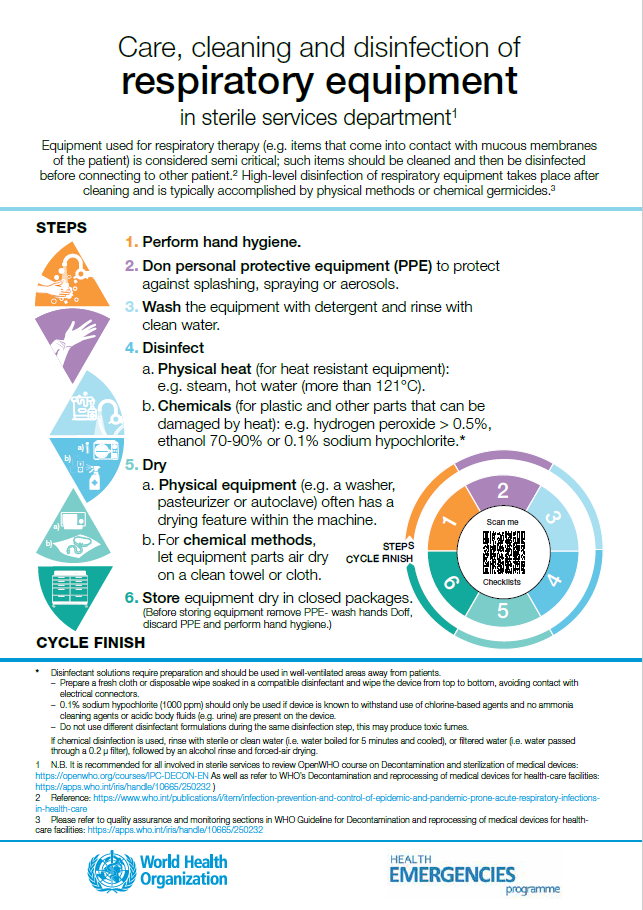
Posters: care, cleaning, disinfection and sterilization

Training Videos
WHO developed a series of training videos for medical equipment related to oxygen therapy. The videos to date include three main steps:
- How to get medical equipment ready to use
- How to perform corrective maintenance
- How to perform preventative maintenance
The equipment in these videos include:
- Pulse oximeter
- Mechanical ventilator
- CPAP/ BiPAP
- Patient monitor
- Oxygen concentrator
- High flow nasal cannula (HFNC)
- Oxygen cylinder
Webinars
Initiatives
.jpg?sfvrsn=113b2e15_11)
Oxygen Access Scale Up
Useful external resources
PATH: COVID-19 Oxygen Needs Tracker

Every Breath Counts Coalition
News
Feature Stories
Multimedia
Contact




